- Home
- About us
- Services
- CFO Services
- Business Advisory Services
- Business Process Re-engineering – BPR
- Business Process Management – BPM
- Standard Operating Procedure - SOP
- Business Gap Analysis
- Mergers & Acquisitions Projections
- Feasibility Projections for Expansion Projects
- SOP Development & Implementation
- KPI Development with C-Level Monitoring
- Business Combinations
- Corporate Restructuring
- Business Planning Support
- Accounting & Bookkeeping Services
- HR & Payroll Services
- Employee Data base
- Attendance record Management
- Overtime & Quota Bonus payment
- Deduction, Promotion & Increments
- Bi-Annual & Annual Staff Evaluation
- KPI Development & Performance Review
- Compliance with relevant Labor Laws
- End of Service Benefits
- Job Description Portfolio (JD's)
- Training and Development
- Standard Forms & Formats Database
- Clients
- Blog
- Contact us
Business Gap Analysis

What is Gap Analysis?
A Business Gap Analysis is a strategic analysis tool that helps to identify the gap between two business states, expected and current, and comes up with an action plan to remove this gap.
Simply, it is a method of assessing the difference between current performance and expected performance.
Business Gap Analysis services help your business in the following ways.
Identify weak points:
If your business did not meet the expected goals and your business did not grow, as you wanted it to, do a Gap Analysis to identify the root cause of failure.
Measure actual resources:
Suppose you have surplus resources at the end of the year. The Gap Analysis helps you to use these resources effectively in the future. Gap Analysis helps identify how everything is performing.
Intercommunicating strategies:
A strategic team can figure out the potential action plan to hit expected goals using Gap Analysis.
How it works
When organizations are not making the best use of capital, resources, and advanced technology, they may not be able to reach their potential growth. Hence Gap Analysis is preferred here. It is important for any type of organizational performance and allows companies to determine where they are standing currently versus where they wish to be.
Gap Analysis was widely used in the 1980s and helps assess susceptibility to a variety of structure movements.
The ”gap” in Gap Analysis is a symbolic space between the current state and the expected state. The four steps in Gap Analysis will help ensure you know precisely what issues you’re facing and how to fix them.
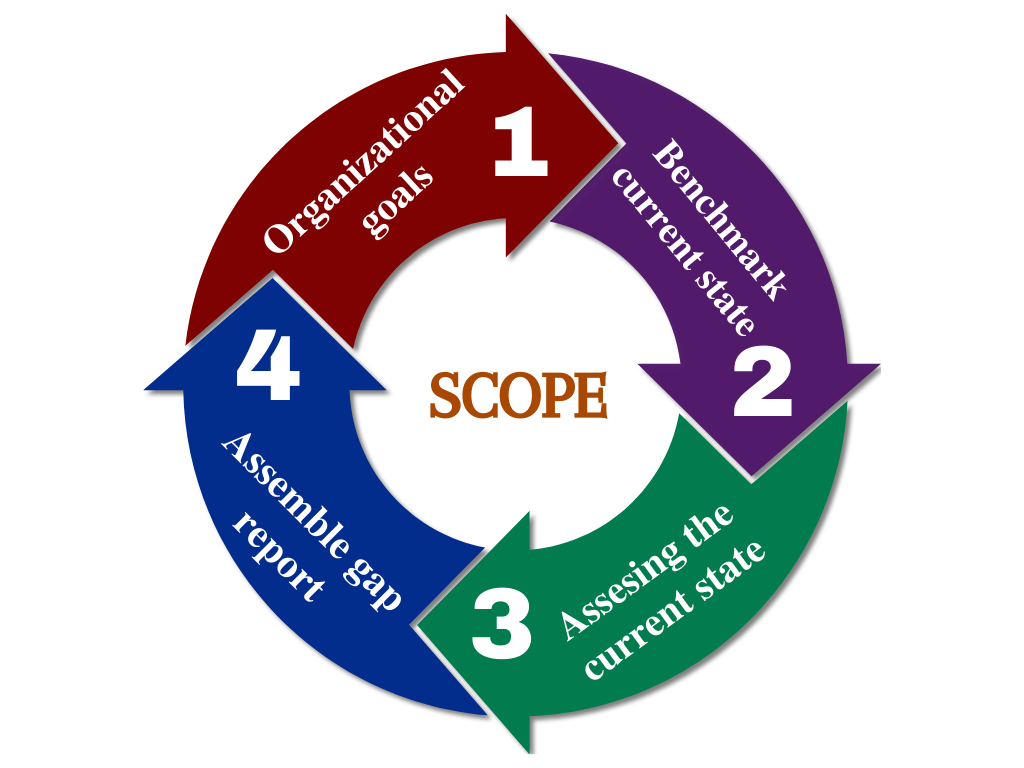
Scope of Gap Analysis
Four steps of Gap Analysis defines
Organizational goals
Benchmarking current state
Assessing the current state
Assemble the gap report
Gap Analysis performs on;
Strategic levels are where you compare the level of your business with the industry standards.
The operational levels are where you compare the current state of business with the expected one.
When to perform a Gap Analysis
Business Gap Analysis is an important project management tool that helps you identify how to get over the default. You can do Gap Analysis any time but specifically, it applies strategically to specific initiatives.
Here are some scenarios where you use Gap Analysis to help you get from point A to point B.
1. During crucial planning
Using a Gap Analysis early in the planning process can help give your team a good starting point when you are looking for a strategic growth plan because it guides your team on how to go from the current state to the expected state. For example, if you are planning a half-year strategy, use Gap Analysis to review what you have achieved in the current half and set your goals to meet future demands.
2. Performance issues
Supposing your business growth is going down the way, Gap Analysis helps you to fix the cause of it. Knowing the root cause your team can perform well to bring you the desired results. For example your production is not meeting the expected product quality, you can use Gap Analysis to identify the problem with machinery or the reactants, and knowing the exact cause helps you to meet goals.
3. When stakeholders need additional context
Gap Analysis provides more contextual information than solid figures when your team is assembling business requirements. Gap Analysis can be a vital tool here.
How to conduct Analysis
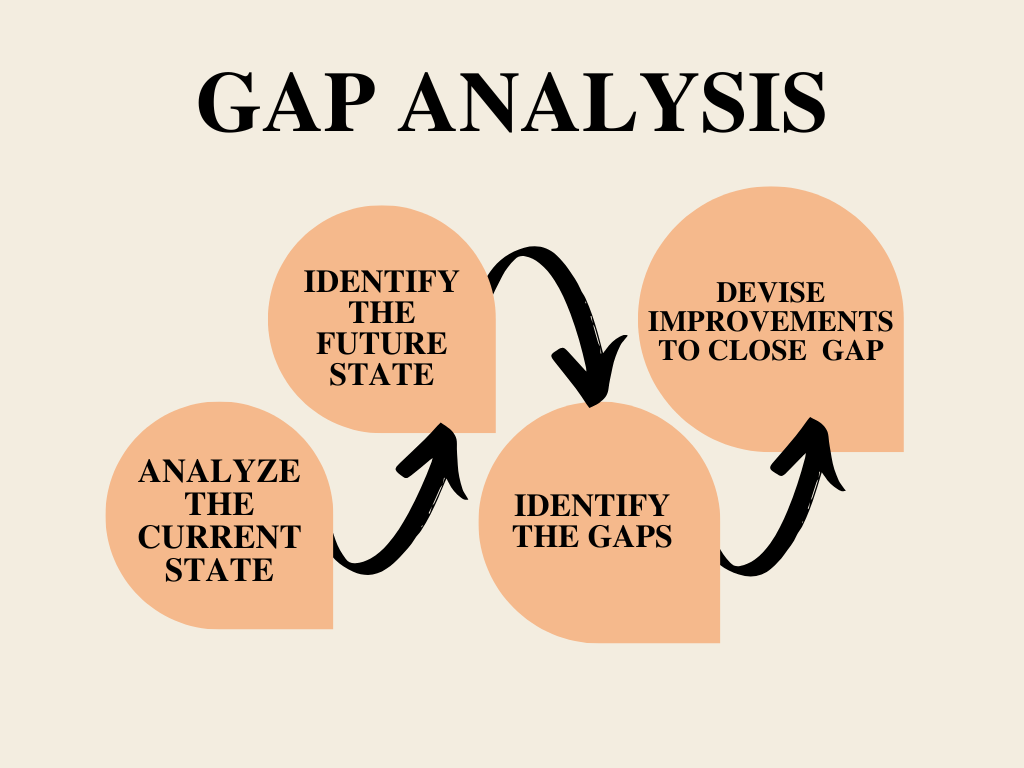
Gap Analysis models break this process into four steps. Regardless of your industry type, follow these four simple steps to meet your business goals.
- Analyze the current state of your business
- Identify future state
- Identify the gaps
- Devise improvements to close the gap
Analyze the current state of your business
First, identify priority, choose which area you want to focus on, and start with the current state where your organization is operating. Collect all the quantitative and qualitative information such as financial records, surveys, or feedback. It may include benefits your company offers to its employees, geographical search area locations, or the products it sells.
Define what is important to your organization. The metrics that you use will be what is most important to the success of the business and describe all your focused areas.
Identify the future state
The future state is also called the stretch goal. Once you have figured out how your organization is currently working, then you need to be ideological. Set your goals or targets where you want to be within a reasonable timeframe. For example, the goal of your soap manufacturing business is to produce 12000 in the quarter year in comparison to 8500 sold this year.
Identify the gaps in business
Now you have recognized the current state of your organization and where you want it to be in the future, it is time to fill this gap. Put all your efforts together to meet your demands. Make yourself equipped to close these gaps and be specific about the gap and dig deep to find the cause of these gaps.
Devise improvements to close the gaps
You have figured out why those gaps occurred, it is time to implement solutions to those gaps. Establish a clear strategy and actionable objectives to help your transition. Evaluate your performance and compare results.
What happens after the Gap Analysis?
After optimistically emerging from the Gap Analysis exercise with great ideas for addressing the failure, execute all your plans to fill the gap.
Here is what needs to happen after Gap Analysis
- Choose a framework that helps to elaborate plans
- Unfold your framework with initiatives, goals, and projects
- Implement your plan and check your progress on the board
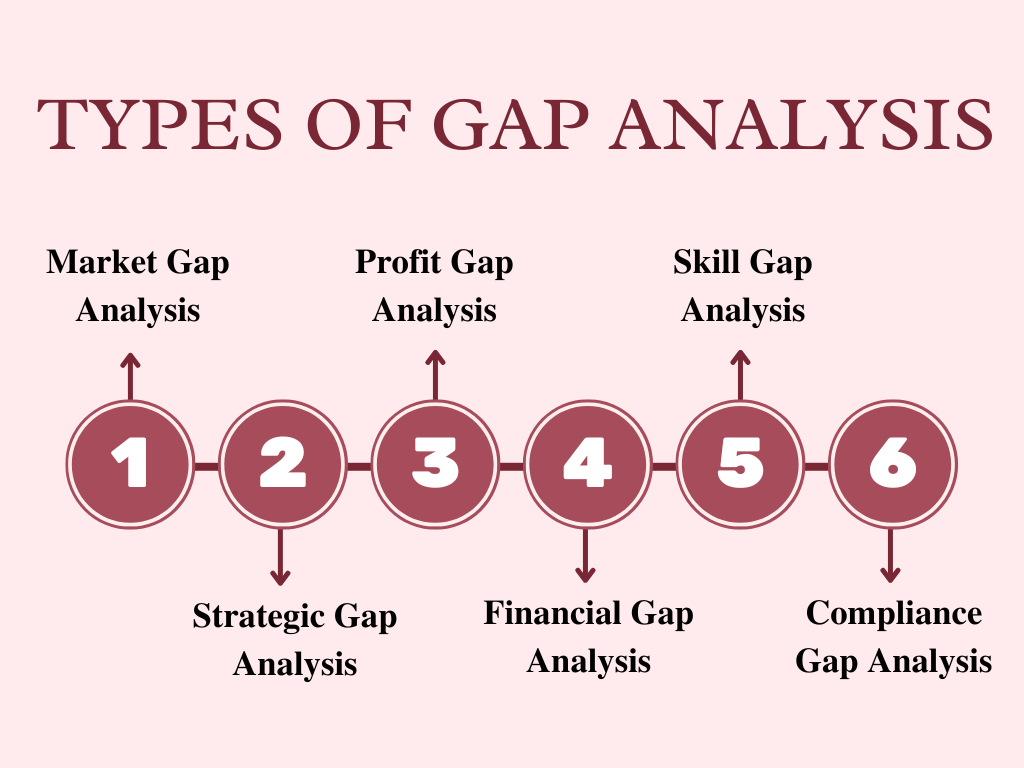
Types of Gap Analysis
Following types of Gap Analysis are performed.
- Market Gap Analysis
- Strategic Gap Analysis
- Profit Gap Analysis
- Financial Gap Analysis
- Skill Gap Analysis
- Compliance Gap Analysis
Market Gap Analysis
Market Gap Analysis is also called product analysis. Market Gap Analysis encompasses market and customer needs. If a company can identify the shortcomings of product supply to the customer, it can take measures to fill the gap. External consultants help here, who are much more experienced in areas of business that the company may not be operating in.
Strategic Gap Analysis
Strategic Gap Analysis is also called performance gap analysis and is an internal review of how a company is performing. This analysis often includes how the company has done against long-term plans.
It is used to measure how the company is surviving against its competitors and points to potential areas for improvement.
Financial Gap Analysis
Financial Analysis aims at shortcomings of financial metrics. It may include margin percentages, overhead costs, and fixed vs. variable components. The ultimate goal is to determine areas in which the competitor is more effectively performing and this information is used further for other analysis types.
Skill Gap Analysis
Skill Gap Analysis aims at the human element instead of looking for financial metrics. It helps to determine the shortfall of human expertise and lack of management skills. This analysis is simply training the company staff to pursue new expertise or skills because this analysis is especially important for companies that have a skill set to maintain a position in the market.
Compliance Gap Analysis
Compliance Gap Analysis evaluates external regulations that command how something should be done. For example, seeking an external auditor to provide opinions on financial statements on accounting and reporting functions.
Compliance Gap Analysis has the intention of meeting all the on-board regulations, and reporting requirements, and avoiding fines.
Product Development Gap Analysis
When a company develops new products, it undergoes Product Development Gap Analysis to know which product qualities will meet market demand and where the product will fall short.
By applying the above analysis the company will perform better to meet market demands hold an appreciating place and successfully conquer future long-term goals.
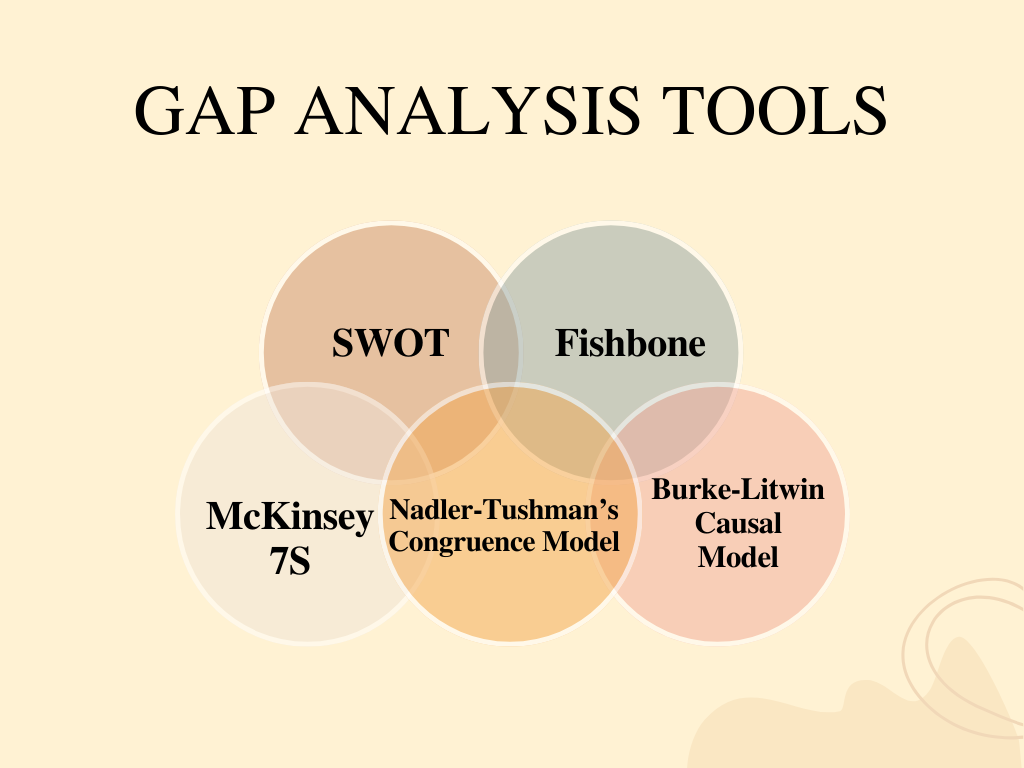
Tools used for Gap Analysis
There are a few Gap Analysis models you can use in business management services.
- SWOT
- Fishbone
- McKinsey 7S
- Nadler-Tushman’s Congruence Model
- Burke-Litwin Causal Model
Benefits of Gap Analysis
Gap Analysis in Business Analysis carries a wide variety of benefits in the following ways.
Enhanced profitability
Companies that assess analysis have resources on hand and work efficiently as it helps to generate more profit and increase revenue growth.
Better manufacturing process
Preventing the gaps in business manufacturing, processes can be performed in a better way increasing the product yield, more efficient delivery, and raw materials being on site.
Operational efficiency
A company can make changes in day-to-day activities by knowing the operational flaws in business.
Secured future planning
By identifying the resources needed, the company plans for gaps and errors before they occur.
Improved market share
By combining the above benefits, a company can have improved market share with increased sales levels.
Gap Analysis examples
The Gap Analysis process is used in different business departments such as sales, accounting, human resources, and customer services.
But specifically, Gap Analysis is used in the following scenarios.
- Product launch
- Supply management
- Sales performance
- Individual assessment
- Productivity
You May Also Like

Feasibility of Expansion Projects
Any business’s growth and development are facilitated by expansion projects. They can aid companies in boosting sales, earnings, and market share. Yet, starting an expansion project can be hazardous and expensive, so organizations should consider its viability before moving forward...

Challenging Liquidation Preferences
Liquidation preferences are terms that investors negotiate with a company when they invest. These terms specify what will happen if the company is sold or goes bankrupt. Typically, liquidation preferences give investors priority over other stakeholders, such as...

Investment Dashboard
The investment dashboard is an integrated panel for tracking, reconsidering, and scaling the performance of investments of the organization. This panel allows the monitoring of investment records following fixed and variable incomes. The process is administrated by an organization’s finance...

Business Process Re-engineering
BPR stands for Business Process Re-engineering. Business process reengineering is a management strategy and a systematic approach to improve product quality and reduce organizational cost, service and speed. It is an act of recreating a core business process and was pioneered in the early 1990s...
