Working Capital Management
Working Capital Management is a business strategy planned to ensure the best utilization of a business’s current assets and liabilities for the company’s effective operation and to maintain sufficient cash flow to meet future short-term goals. Working capital management refers to the set of activities that make sure the company has sufficient resources for day-to-day operations. The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) administrates this process with the organization’s finance department.
Importance of working capital
If a company has sufficient working capital, it continues to pay its employees and suppliers. Successful management of working capital is essential, otherwise, even profitable businesses tend to collapse due to the inability to meet short-term goals. It improves company cash flow management. Management of working capital includes both accounts receivables and account payables. Improving working capital boosts the operational efficiency of the business.
How to operate working capital
The formula for working capital is;
Working capital = Current assets – Current liabilities
Current assets are all those assets of the company which can be converted into cash and are quite liquid including accounts receivables and current liabilities are the bills that are due within one year. The goal of working capital management is to ensure that the company has sufficient cash on hand to pay.
Components of Working Capital
A well-run firm manages its short-term debt and current and future operational expenses through its management of working capital, the components of which are; inventories, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and cash.
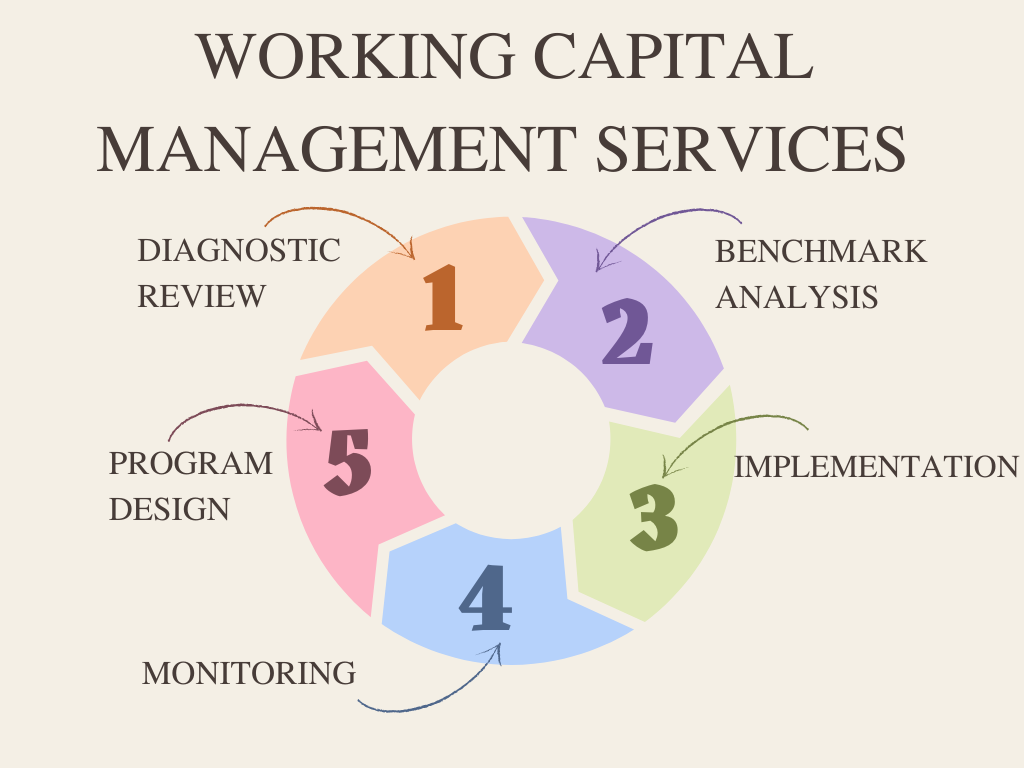
Working Capital Management Services include;
- Diagnostic review
- Benchmark analysis
- Program design
- Implementation
- Monitoring
Working Capital Ratios
Several ratios are available that aid managers in supervising working capital which include day sale outstanding, current ratio, and inventory turnover ratio. All these terms are given below;
Days sales outstanding
Days sales outstanding arbitrate the efficiency with which a business collects its account receivables. Days sales outstanding are calculated by dividing account receivables by the annual revenue figure and then multiplying the result by the number of days in the year.
DSO = (Accounts receivable ÷ Annual revenue) × Number of days in the year
Current ratio
One of the important working capital measurements is the current ratio, which compares current assets to current liabilities. If the current assets figure is higher than the current liabilities, then a business should be able to settle its short-term obligations but a problem with a current ratio is that the inventory component can be difficult to liquidate.
Inventory turnover ratio
The inventory turnover ratio is also an important factor. Inventory turns should be high which ensures that the company can sell off its inventory within a short period.
Inventory turnover is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold for the year by the ending inventory.
Inventory turnover = Annual cost of goods sold ÷ Average inventory
A high inventory turnover ratio indicates that the business does not have sufficient cash to pay for the inventory needed to run its operations. When this is the case, the firm will probably not be able to maximize its sales.
Working Capital and the Balance Sheet
We evaluate working capital from current assets and current liabilities which are reported on the company balance sheet. The balance sheet is a primary financial statement that a business produce and reports its asset, liabilities, and shareholder equity.
Elements included in working capital are;
- Cash
- Treasury bills
- Short-term investment
- Account receivables
- Inventory
- Prepaid expenses
- Advance payments
- Other receivables such as income tax funds
Objectives of working capital
Working capital is an important criterion for business because it ensures that the company has sufficient amount to make payments. Effective management of working capital is not easy and there are multiple objectives for managing working capital which are given as follows;
Optimization of capital performance:
An important objective of working capital is to optimize the effectiveness of capital usage which is;
- Minimizing capital cost
- Maximizing capital return
Minimizing capital resources is achieved by reclaiming capital that reduces the need for borrowing. Later involves ensuring the return on investment of spare capital outweighs.
Growing business:
Using short-term assets effectively is important. The business may not be as profitable as it could be if your company assets are tied up in account payables.
Meeting obligations:
The primary goal of working capital is to ensure that the company always has enough liquid assets to meet short-term obligations. Unexpected costs also need to be factored into the approach because these are also considered obligations.
Ways to increase working capital management
Tactics to increase effective working capital management include;
- Taking on long-term debt
- Selling illiquid assets
- Analyzing and reducing expenses
- Optimize inventory management
- Automate account receivables and payment monitoring

Working Capital Management Solutions
Following are solutions to working capital management that many companies adopt under CFO guidance.
- Flexible funding
Working capital providers offer flexible funding allowing buyers to move flawlessly between supply chain finance and dynamic discounting models which means that companies can adopt their varying working capital needs.
-
Dynamic discounting
Dynamic discounting is another solution that buyers use to provide early payment to suppliers but without third-party funders. This enables suppliers to reduce their DSO and allows buyers to achieve a risk-free return on excess cash.
-
Supply chain finance
Supply chain finance is also known as reverse factoring. It is a way of offering suppliers early payment via one or more third-party funders. Suppliers can improve days sales outstanding(DSO) when paid sooner. Also, buyers preserve their working capital by paying with agreed terms.
-
Cash flow forecasting
Companies can plan for upcoming cash gaps by forecasting future cash flows such as account payables and account receivables. It ensures better use of surpluses. The more precisely you predict your cash flow, the more well-informed working capital management decisions will be.
-
Inventory management
Smart execution of inventory management solutions helps to improve balance sheet position or working capital position. It is achieved by reducing long lead times, assuring access to safety stock, and making this process more transparent.
-
Electronic invoicing
Working Capital Management benefits from electronic invoicing. By simplifying the invoicing process, you can reduce the risk of errors and automate manual processes. Make sure all our customers receive the invoice as early as possible which eventually means you get payments on time. These methods allow companies to turn purchase orders into invoices automatically.
You May Also Like

Treasury Management
Treasury management is the process of managing a company’s daily cash flows and larger-scale decisions made when it comes to finances. It is a key component of business operations. In the business landscape, the importance of treasury management cannot be denied. Treasury management...

Tips For Managing Business Through Finance
Managing a business through finance is one of the most crucial aspects of any organization. It is important to make sure that the financial resources are utilized in the best possible way to ensure the success and growth of the business. The management...
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
A Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is a set of written instructions that describes activities necessary to complete the task under industry regulations. A Standard Operating Procedure is a document containing step-by-step instructions. SOP means simply a step-by-step...

Business Process Re-engineering
BPR stands for Business Process Re-engineering. Business process reengineering is a management strategy and a systematic approach to improve product quality and reduce organizational cost, service and speed. It is an act of recreating a core business process and was pioneered...
